This document provides detailed instruction for preparing the files, and steps
to run Chromaligner. Chromaligner requires three files, data file, parameter
file, and index file for running alignment algorithms in chromatograms. Due to
the different output file format provided by different equipments, users need to
follow Chromaligner format (highlighted in black)
to run it successfully. Here we provide three demo tutorials and attach the links
of the example files in the last paragraph of each tutorial:
Click to see demo 1 (Alignment without any constraints).
Click to see demo 2 (Alignment with user-specified peaks).
Click to see demo 3 (Alignment with diode array detector data).

Chromaligner is a tool for chromatogram alignment. It could be used for chromatograms generated by various chromatographic methods such as high performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Time shift is a frequently encountered problem in gradient elution or capillary electrophoresis. Chromaligner used a constrained chromatogram alignment method to resolve this issue.
Chromaligner aligns chromatograms based on correlation optimized warping (COW)
with optional alignment on predefined peaks. The inputs of Chromaligner include
a set of chromatograms comprising intensity, retention time and constraints if
there are any. The constraints are the common user-defined peaks (or predefined
peaks) or automatically assigned by Chromaligner by mapping the full spectrum.
The outputs files from Chromaligner are aligned chromatograms along with
overlaid spectrum (before and after alignment).

Chromaligner aligns chromatograms based on correlation optimized warping with optional alignment on predefined peaks. It provides three different alignment methods to predefine peaks. Different method has its unique procedure for alignment. All procedure requires three types of files, an index file, raw data files and parameter files . All the required files must be in the ".txt" extension.
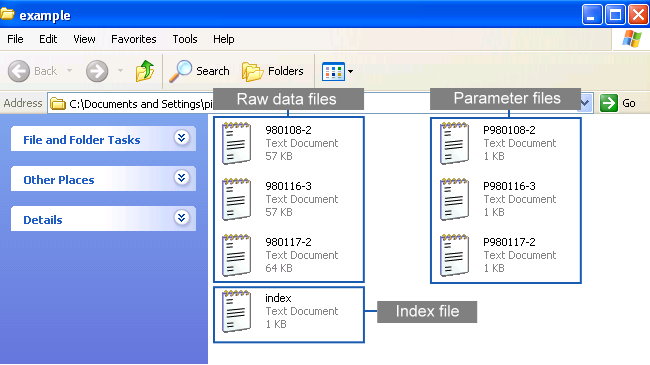
The following figure shows a example folder containing all the required files
for Chromaligner :


The Chromaligner reads full-scan data(Ex: CE, HPLC) in tab delimited format (Text file type, extension: txt)
Different instruments generate different output file formats, and most of them
have special extensions such as are, asc etc. These files can usually be opened
by Microsoft office Excel.
Click to see how to save raw data as a "txt" file.

Chromaligner provides three different alignment methods: alignment without any constraints, alignment with user-specified peaks, alignment in different segments, alignment with diode array detector. Different methods require different raw files.
First three methods require retention time to intensity file as raw data. Fourth method, alignment with diode array detector requires DAD file. Chromaligner only accept tab delimited files(Text file type, extension: txt). Click to see how to save raw data as a "txt" file.

The files required in this method are the
retention time to intensity files. In each file,
each row represents a retention time (machine time frame) and the column
represents the corresponding intensity. The direct output from the instrument
may look like the following figure:
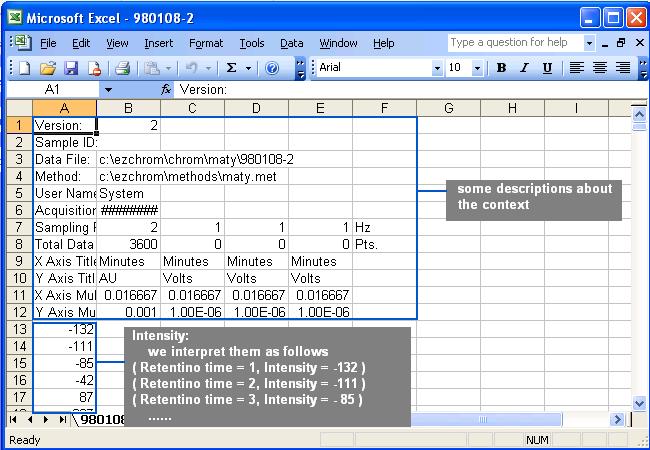
The only information needed is the intensity.
Delete the descriptions in the file before saving the files into txt format.
The processed files should look similar to the following figure:
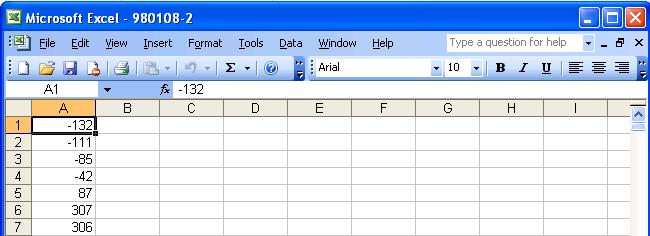
The "first column" should always contains the
intensities
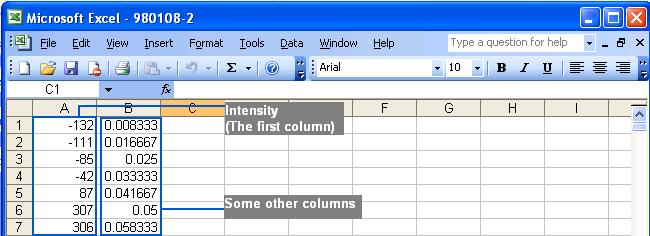
extra columns may be added by the users in the files. However, extra columns
will not be used by Chromaligner. The following figure shows the flexibility:

The files required in this method are the same retention time to intensity
files
as in the method "alignment without any constraints".
Click to see the details.

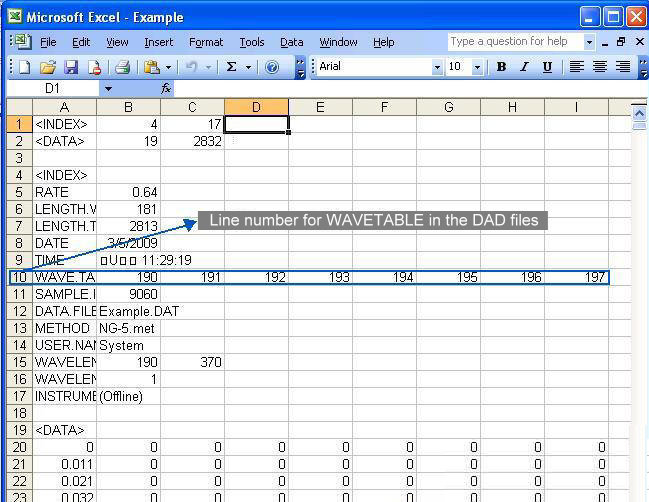
The files required in this method are DAD files.
It looks like the following figure:

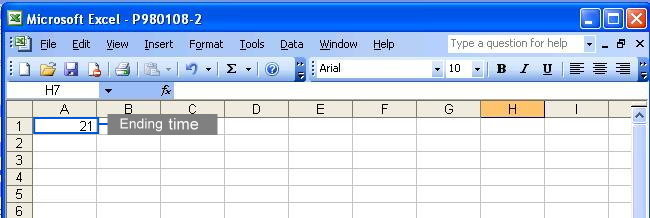
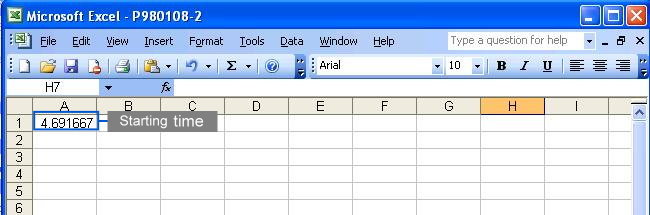
Parameter file contains information of the starting and the ending time as well as the predefined peaks in time (min).
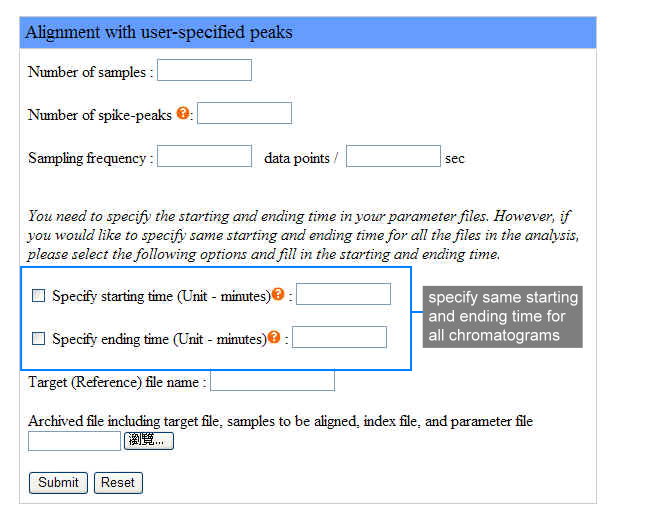
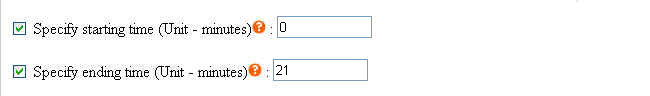
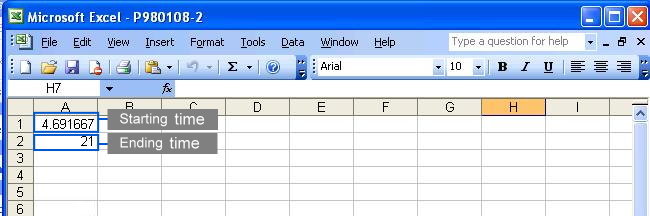
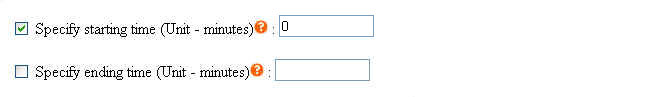
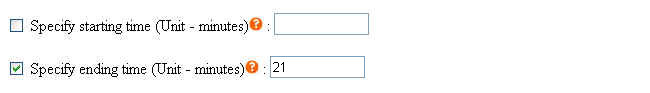
To eliminate unwanted sections at the beginning and the end of each chromatogram where noises are located, users must specify the starting and ending time in the parameter files (Click here to see an example). Each parameter file corresponds to each chromatogram. If you wish to specify same starting and ending time for all your chromatograms, you may do so at the webpage by selecting the checkbox. Click to see where to check the option.

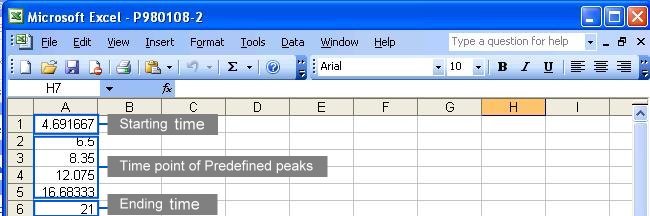
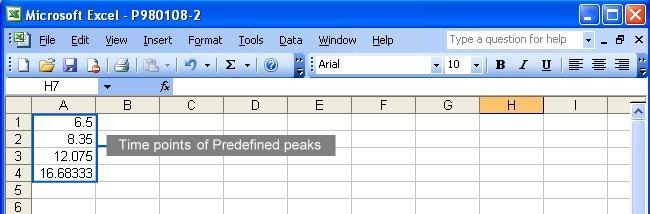
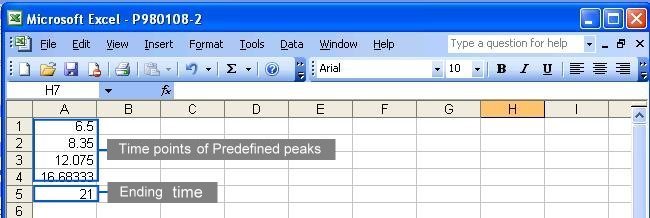
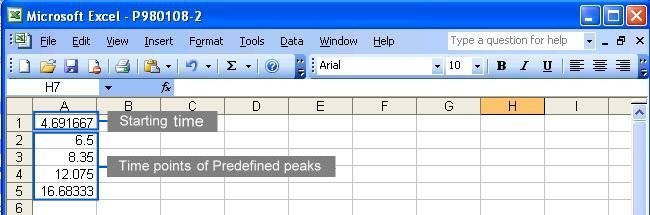
A complete parameter file should contain three information
in the order of
the starting time, the time points of predefined peaks
and
the ending time. The default time unit of measurement
is minutes. See the following figure for the content in a parameter
file:
Different alignment method may require different inputs in the parameter files, please see parameter setting under each alignment method below.

Each chromatogram should have its parameter files to better adjust the peak shifts in each chromatogram.
For each parameter file, append ‘P’ (in capital) before the corresponding raw data file name. For example, a parameter file should be named as "P980108-2.txt" for a raw data file named "980108-2.txt".

This method uses the original correlation optimize warping alignment, no predefined peaks are needed. There are many ways to specify the starting and ending time of each chromatogram. Graphical tutorials are as follows:


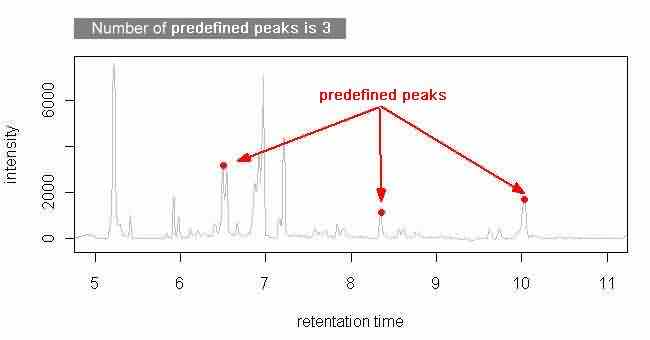
This method takes the predefined peaks for raw data in each corresponding parameter file. Users have to specify at least one predefined peak in each parameter file to use this method. All predefined peaks must be specified in the parameter files (see following figures); however, there are several ways to specify the starting and ending points of each chromatogram.






This method is similar to last method. After users specify some constraints through the web page, Chromaligner will find the predefined peaks automatically. Parameter files setup is the same as in the method “alignment without constraints”. Click here to see how.

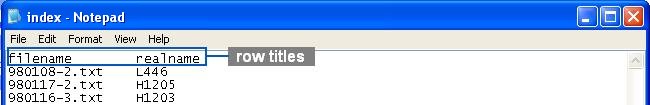
An index file gives a complete list of raw data file. Chromaligner automatically checks whether the raw data and the corresponding parameter files were uploaded successfully.

Users must list all file names in an index file entitled “index.txt”. The first row in the index file is the title of each column. The first column has to be the raw data files' names you uploaded. You may also specify names for each file as in the following figure.
Note: each column can be separated by "tab" or "space", but Chromaligner does not accept any space or tab in the file name.

To simplify the process, users have to archive all required files, index file, raw data files, and corresponding parameter files, in ONE ZIP file before uploading the zip file to Chromaligner. ZIP is an archive file format to reduce the file size for uploading. Chromaligner does not accept files in RAR format.

To archive all files in the zip format, we suggest the following steps. 1) put index file, raw data files, and corresponding parameter files in into one folder, 2) select all the files and right-click on one of the files. 3) if you have ZIP program installed, you can see the “extract” function on your the right-click list; If you don’t have zip program installed, Windows do have an built-in ZIP archiver in your computer. To download a zip program, click here.
The following figure shows how to archive files to one ZIP file by the Windows default ZIP archiver.
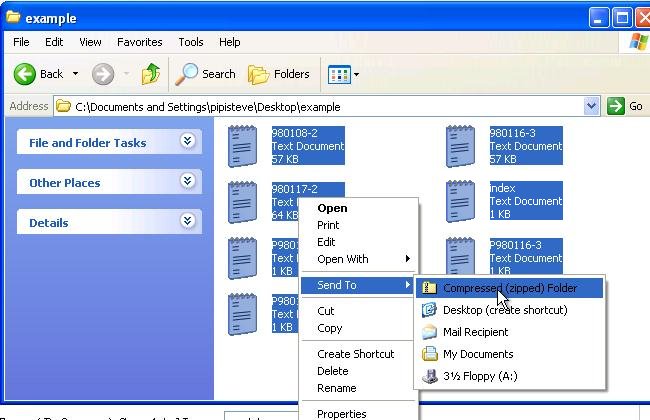
Please archive the files directly into a ZIP file without the folder.

Chromaligner webpage interface has different input forms to be filled with each alignment method. In this section, we provide some example files and graphical tutorials for users.

We provide an example of aligning two sample files with a target file without any constraint. Samples include the target file and sample files to be aligned, so the number of samples is 3. The instrument sampling frequency is 2 data points per second. We specify the same starting time 1.5 minutes for all the chromatograms. And we prepare the corresponding parameter file containing different ending time information of each chromatogram.
The target file name is "980108-2.txt". The file names of samples to be aligned are "980117-2.txt" and "980116-3.txt". Users don't have to specify the file names of samples to be aligned in the webpage interface but the target file name is required.
The following figure shows how to set the parameters in the webpage interface for the example as we described:
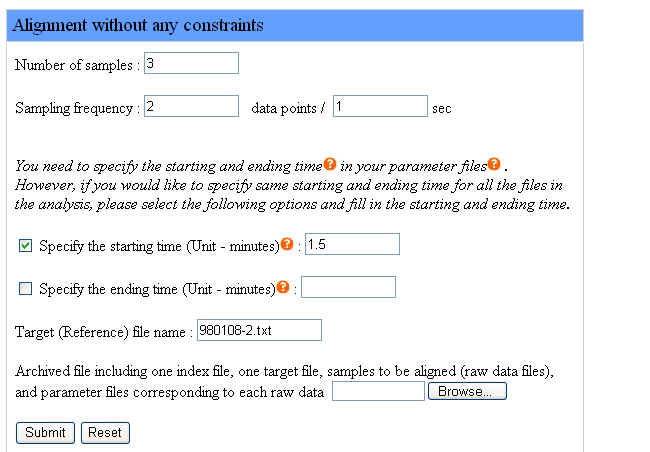
Please click here to download the example file above and click the "Browse" button to upload this file. After filling the form in the webpage interface, uploading the example file and clicking the "Submit" button, users are ready to run Chromaligner.

We provide an example of aligning two sample files with a target file with user-specified peaks. Samples include the target file and sample files to be aligned, so the number of samples is 3. We use 4 user-specified peaks as constraints to do alignment, specify the time points of these peaks in the corresponding parameter files. The instrument sampling frequency is 2 data points per second. We specify each starting and ending time of each chromatogram in the corresponding parameter file and leave all the option box unchecked.
The target file name is "980108-2.txt". The file names of samples to be aligned are "980117-2.txt" and "980116-3.txt". Users don't have to specify the file names of samples to be aligned in the webpage interface but the target file name is required.
The following figure shows how to set the parameters in the webpage interface for the example as we described:
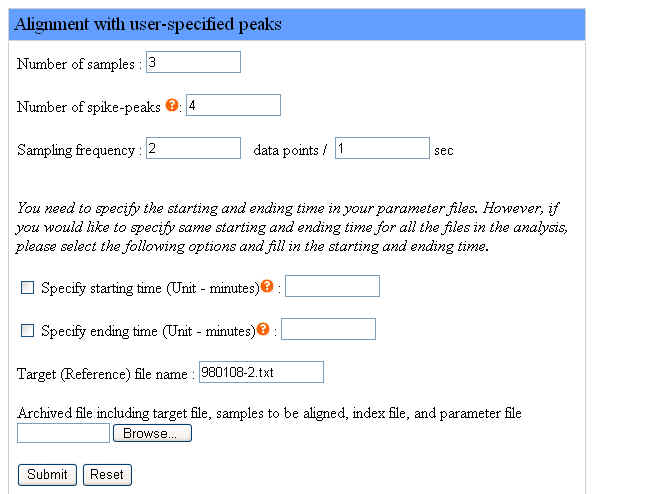
Please click here to download the example file above and click the "Browse" button to upload this file. After filling the form in the webpage interface, uploading the example file and clicking the "Submit" button, users are ready to run Chromaligner.

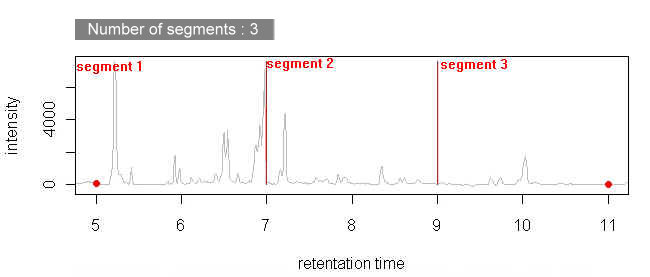
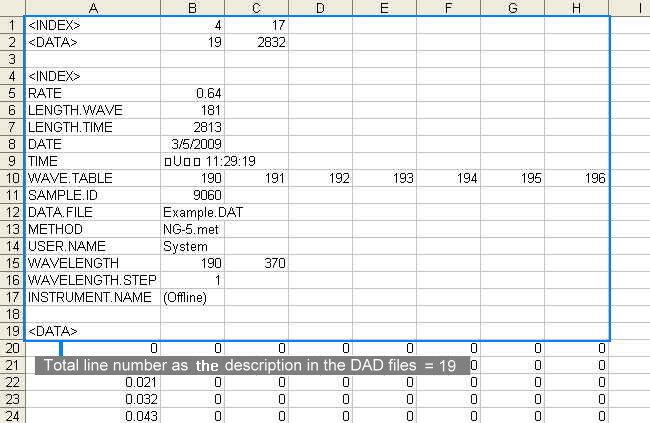
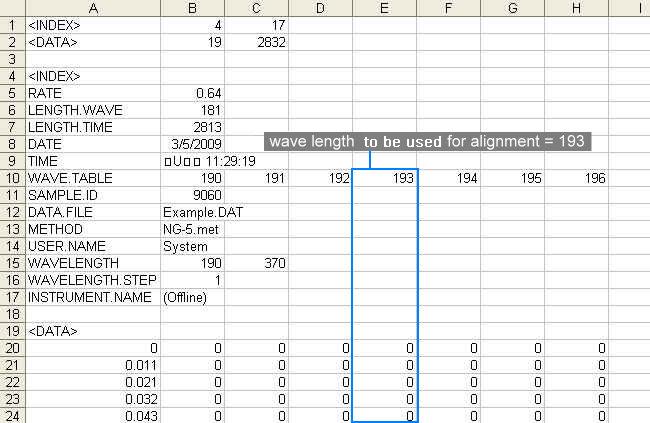
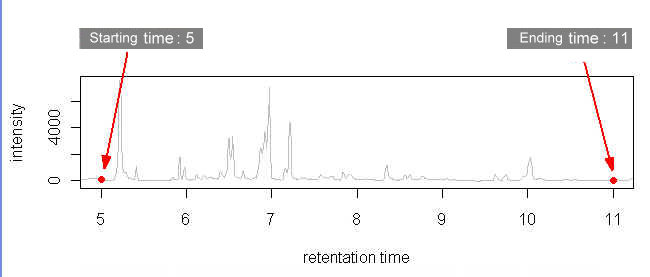
We provide an example of aligning two sample files with a target file with user-specified peaks. Samples include the target file and sample files to be aligned, so the number of samples is 3. We define the number of segments to be aligned is 3. The total line number as the descriptions in the DAD files is 19. We set 10 to be the line number for WAVETABLE in the DAD files and 210 to be the wave length to be used for alignment. The instrument sampling frequency is 1 data point per 0.64 second. We specify the same starting time 0 minute and the same ending time 20.6 minutes for all the chromatograms.
The target file name is "sample01.txt". The file names of samples to be aligned are "sample02.txt" and "sample03.txt". Users don't have to specify the file names of samples to be aligned in the webpage interface but the target file name is required.
The following figure shows how to set the parameters in the webpage interface for the example as we described:
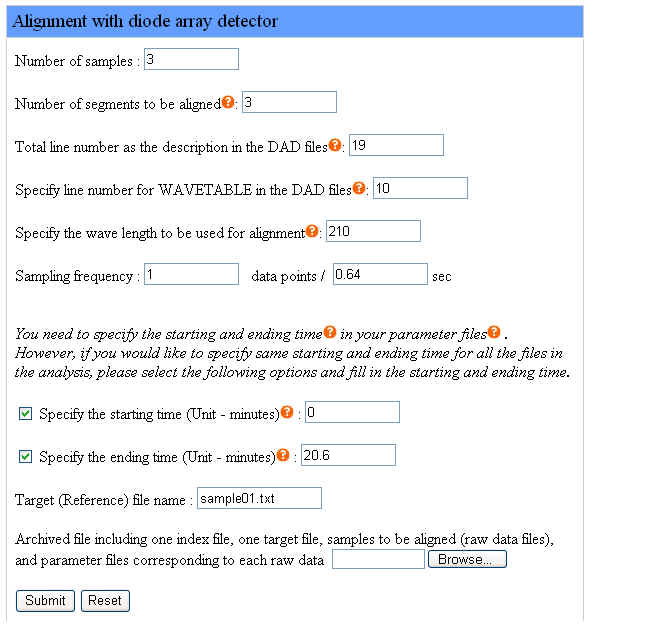
Please click here to download the example file above and click the "Browse" button to upload this file. After filling the forms in the webpage interface, uploading the example file and clicking the "Submit" button, users are ready to run Chromaligner.

Chromaligner exports three different files : retention to intensity files, chromatograms and full data.
When Chromaligner finished the alignment process, a result page will be displayed as follows:


Users can download retention time to intensity files by clicking the first link as in the following figure:

After clicking the link, the downloaded file is a ZIP file named "aligned_retentiontime_file" containing all the raw data after alignment as the following figure:
No matter whether the raw data are DAD files or retention time to intensity files, the aligned files are all transformed into retention time to intensity files. For each retention time to intensity files after alignment, we append "-processed" in the corresponding original raw data file name.
After extracting the downloaded ZIP file, the content of the extracted folder should look similar to the following figure:
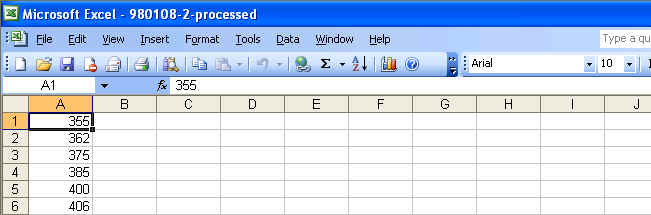
You can open these aligned files with Microsoft Excel. Graphical tutorials are as follows:

Users can download chromatograms by clicking the second link as in the following figure:
After clicking the link, the downloaded file is a ZIP file named "chromatograms" containing all the chromatograms (before and after alignment) as seen in the following figure:
Chromatograms exported from Chromaligner are image files with the extension ".png". The files containing chromatograms before alignment are named as their corresponding raw data file names. For chromatograms after alignment, Chromaligner append "-processed" in the corresponding raw data file name.
After extracting the downloaded ZIP file, the content of the extracted folder should look similar to the following figure:
You can view these chromatograms with softwareis supporting ".png" file extension. The following figure is an example of two overlaid chromatograms with "Windows Picture and Fax Viewer" (a software embedded in Microsoft system):
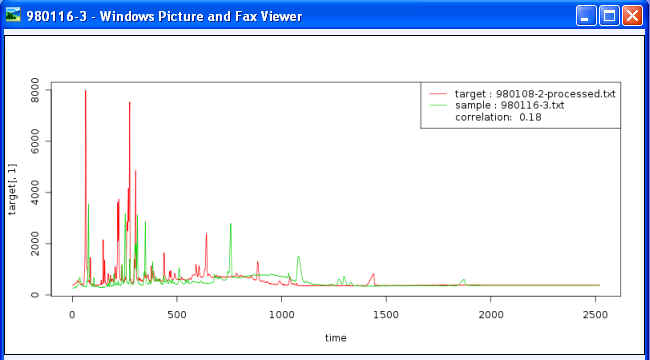
Each image file contains two curves with two different colors: one for the target chromatogram and the other for sample. Users can observe the peak shifts between the target and sample intuitively in this overlaid graph.
Legends on each image file contain the following information: 1) target file name and the corresponding colors in the chromatogram, 2) file name of the sample aligned to the target chromatogram and its corresponding color in the chromatogram and 3) Pearson correlation coefficient between the target and the sample data.

Full data include retention time to intensity files (after the alignment process) and chromatograms (before and after alignment). Users can download the full data by clicking the last link as seen in the following figure:

The downloaded file is a ZIP file named "fulldata" as in the following figure:
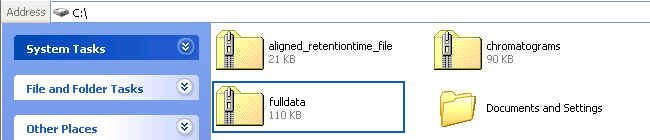
After extracting the downloaded ZIP file, the content of the extracted folder should contain two folders similar to the following figure:
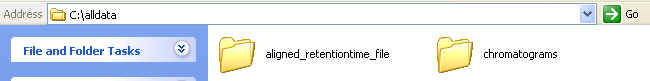
The contents of the "aligned_retentiontime_file" folder are the retention time to intensity files after alignment. The contents of "chromatograms" folder are the chromatograms (before and after alignment).

In this section, we include some examples and tips for operation.

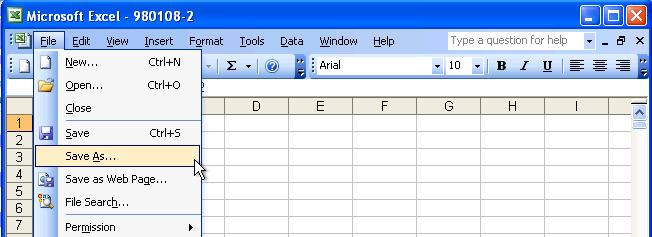
Here is an example to use Microsoft Excel to convert a file to TXT file format.
Launch Excel, choose "File" and then "Open" option as follows:
Change the "File of types" option on at the bottom of the window into "All Files" and select the file you want to convert.
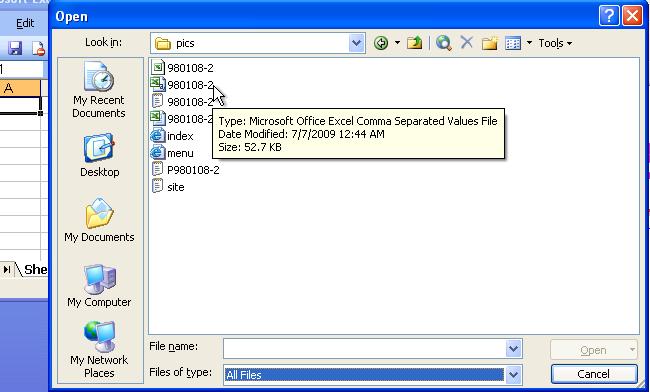
If the file was opened successfully, it should look like the following figure. In this example, it is a raw data file containing retention time to intensity information.
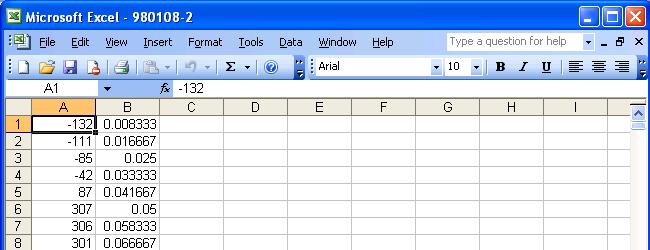
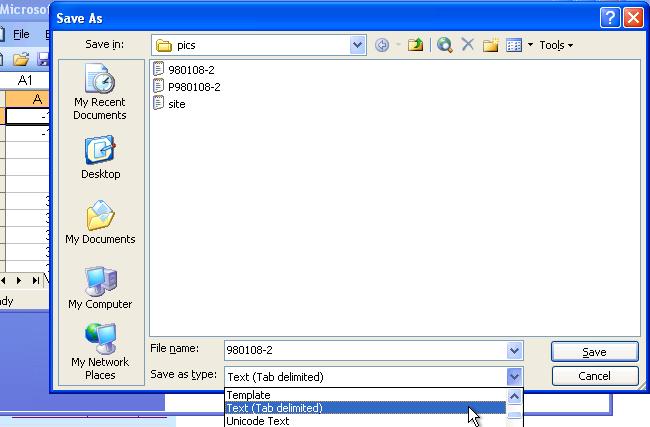
Now, click "File" on the upper left corner again and use "Save as" option. Click the "File of types" into "Text"(tab delimited), then the "Save" button and it is done!